What is Stateless
Stateless ESXi refers to a VMware ESXi configuration, a popular hypervisor used for virtualization. The ESXi host operates without a local disk or persistent storage in a stateless ESXi configuration. Instead, it boots over the network using network booting or remote booting.
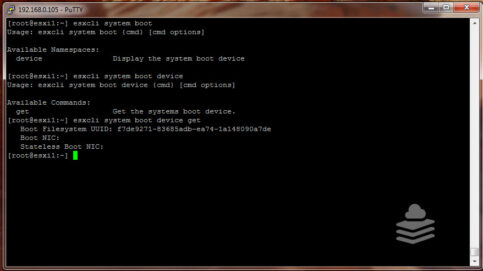
In a stateless ESXi setup, the host’s boot image is stored and retrieved from a centralized location, such as a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server or a shared storage location. The host’s configuration, including network settings, virtual machine settings, and other parameters, is also stored centrally and retrieved during the boot process.
When an ESXi host is stateless, it doesn’t retain any changes or modifications made during its operation. Any changes to the host’s configuration or state are discarded after a reboot or shutdown. This means that the host always starts in a clean and consistent state.
Administrators typically use tools like Auto Deploy to maintain stateless ESXi hosts, which allows for automated provisioning and deployment of hosts, vSphere PowerCLI (PowerShell command-line interface), or the vSphere Web Client for configuration management.
Stateless ESXi hosts offer simplified deployment, centralized configuration management, scalability, and reduced disk-related tasks. However, they also require a robust network infrastructure, careful planning, and configuration management to ensure proper operation and stability.
It’s worth noting that stateless ESXi hosts are not the only configuration option available. Traditional disk-based ESXi hosts, where the host’s boot image and configuration are stored locally on disks, are also widely used, depending on the requirements of the environment. The choice between stateless and disk-based ESXi hosts depends on infrastructure capabilities, operational needs, and security considerations.
What are the benefits?
- Reduced Deployment Time: Stateless ESXi hosts can be deployed quickly and easily because they do not require individual disk configuration. By leveraging network boot and configuration methods like PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) or Auto Deploy, administrators can provision new ESXi hosts rapidly.
- Simplified Management: With stateless ESXi hosts, there is no need to manage local disk configurations, such as formatting, partitioning, or managing disk failures. This reduces the complexity of host management and simplifies ongoing maintenance tasks.
- Centralized Configuration: The configuration of stateless ESXi hosts is stored centrally, typically on a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server or in a shared storage location. This centralized configuration allows administrators to easily manage and update host configurations across multiple hosts from a single location, ensuring consistency and reducing the risk of configuration errors.
- Enhanced Scalability: Stateless ESXi hosts offer greater scalability because they can be provisioned and deployed rapidly. This is particularly beneficial in environments where frequent host provisioning or dynamic scaling is required, such as in virtualized data centers or cloud infrastructure.
- Improved Resource Utilization: Since stateless ESXi hosts do not have local disks, the host does not consume the physical disk resources. This allows for more efficient utilization of storage resources, as the disk space can be dedicated entirely to virtual machines (VMs) or other storage needs.
- Simplified Disaster Recovery: Replacing a stateless ESXi host is straightforward in case of failure. The new host can be provisioned quickly using the centralized configuration, reducing downtime and simplifying the disaster recovery process.
- Standardization and Consistency: With stateless ESXi hosts, the host configurations are standardized and consistent across the environment. This reduces the likelihood of configuration drift, simplifies troubleshooting, and improves overall system stability.
When not to choose Stateless
- Unreliable Network Infrastructure: Stateless ESXi hosts heavily rely on network boot and configuration. If your network infrastructure is unreliable or prone to frequent outages, it can negatively impact the functionality and stability of stateless hosts. In such cases, it may be more appropriate to use disk-based ESXi hosts with local storage.
- Limited or Slow Network Connectivity: Stateless ESXi hosts require a fast and reliable network connection for efficient booting and configuration retrieval. If your network connectivity is limited or slow, it can significantly affect the performance and responsiveness of stateless hosts. It’s important to ensure that your network infrastructure can adequately support the requirements of stateless ESXi hosts.
- High-Security Requirements: In environments with stringent security requirements, diskless ESXi hosts may not be the preferred option. Stateless hosts rely on centralized configuration stored in a shared location, which could present a potential security risk if improperly secured. Disk-based ESXi hosts, where configurations are stored locally, may be more suitable for environments with strict security controls.
- Compatibility Limitations: Some hardware configurations or specific use cases might not be compatible with stateless ESXi hosts. Certain hardware features or functionalities may require local storage, such as specific driver requirements or advanced disk-based features. It’s important to verify the compatibility and supportability of stateless ESXi hosts with your hardware and software requirements.
- Complexity and Operational Overhead: While stateless ESXi hosts simplify management and reduce disk-related tasks, they introduce additional complexity regarding network boot and configuration management. Setting up and maintaining a robust infrastructure for network booting, TFTP servers, and configuration management can require additional resources and expertise. If your organization lacks the necessary skills or resources, disk-based ESXi hosts might be more practical.
Conclusion
Stateless ESXi hosts offer significant benefits in rapid deployment, simplified management, resource utilization, and disaster recovery. However, they require a reliable network infrastructure, careful security considerations, and additional complexity in configuration management. Decision-makers should evaluate their organization’s requirements and constraints to determine whether stateless ESXi aligns with their virtualization goals.