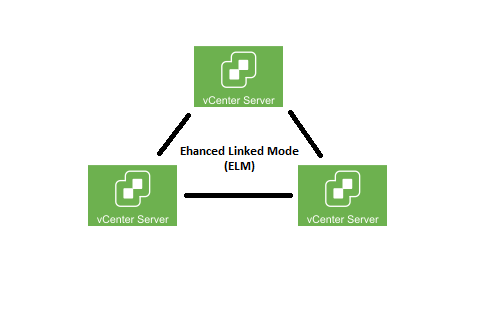
vCenter Enhanced Link Mode (ELM) is a feature that allows you to link multiple vCenter Server instances together, creating a unified management environment. It enables the centralized management and monitoring of multiple vSphere environments, providing a single pane of glass for administrators to control their virtual infrastructure.
When vCenter Server instances are linked through Enhanced Link Mode, they form a logical federation, allowing administrators to view and manage all the linked vCenter Server instances from a single vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client interface. This eliminates the need to switch between different vCenter Server instances and provides a holistic view of the entire virtual infrastructure.
Enhanced Link Mode offers several key capabilities and benefits:
- Unified Management: By linking vCenter Server instances, administrators can manage and monitor multiple vSphere environments as a single entity. This simplifies administrative tasks, reduces complexity, and improves operational efficiency.
- Scalability: Enhanced Link Mode enhances the scalability of the vCenter Server by allowing you to manage larger environments. You can link up to 15 vCenter Server instances together, supporting thousands of hosts and virtual machines.
- Cross-vCenter vMotion: Enhanced Link Mode enables cross-vCenter vMotion, which allows you to migrate virtual machines (VMs) between different vCenter Server instances without shared storage or a single vCenter Server domain. This facilitates workload mobility and resource optimization across vSphere environments.
- Content Library Sharing: ELM enables the sharing of Content Libraries across linked vCenter Server instances. Content Libraries provide a centralized repository for storing VM templates, ISO images, and other files. With ELM, you can share and synchronize these libraries across multiple vCenter Server instances, ensuring consistency and ease of deployment.
- High Availability: By linking multiple vCenter Server instances, Enhanced Link Mode enhances high availability capabilities. If one vCenter Server instance becomes unavailable, administrators can still manage and monitor the environment through other linked instances.
- Resource Pooling and Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS): ELM allows resource pooling and Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) across linked vCenter Server instances. You can create resource pools spanning multiple vCenter Server instances and leverage DRS to optimize resource utilization across the entire linked environment.
How do I configure it?
Follow a series of steps to configure vCenter Enhanced Link Mode (ELM). Here is a general outline of the configuration process:
- Ensure Prerequisites:
- Verify that all vCenter Server instances you want to link are running compatible versions. They should be part of the same vSphere version family.
- Ensure that networking connectivity is established between the vCenter Server instances, including DNS resolution, firewall rules, and network routing.
- Deploy and Install vCenter Server:
- Deploy and install vCenter Server instances individually according to the VMware documentation for each version.
- During the installation, provide appropriate configuration details, such as the deployment type, network settings, and database options.
- Configure vCenter Single Sign-On (SSO):
- Set up and configure vCenter Single Sign-On (SSO) on each vCenter Server instance. This involves creating an SSO domain and specifying a common SSO site name for all instances.
- Ensure that the SSO configuration settings, such as the SSO domain name and passwords, are consistent across the linked vCenter Server instances.
- Link vCenter Server Instances:
- Use the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface (VAMI) or vSphere Client to log in to each vCenter Server instance separately.
- Navigate to the vCenter Server configuration settings and select the option to join or link the vCenter Server to an existing SSO domain.
- Provide the appropriate SSO domain details, such as the SSO site name, domain name, and administrator credentials.
- Verify the Link:
- After linking each vCenter Server instance, verify the link status. Ensure that all the linked vCenter Server instances are displayed and accessible from the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
- Configure Permissions and Roles:
- Review and configure the appropriate permissions and roles for administrators, users, and groups across the linked vCenter Server instances. This ensures proper access control and management capabilities for each administrator.
- Validate and Test:
- Perform comprehensive testing to ensure that all linked vCenter Server instances can be managed from a single vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
- Verify the functionality of features such as cross-vCenter vMotion, Content Library sharing, and resource pooling.
Disadvantages of ELM
While Enhanced Link Mode (ELM) in vCenter Server offers several benefits, there are also a few potential disadvantages to consider:
- Complexity: Implementing and managing Enhanced Link Mode can introduce additional complexity to your vSphere environment. Configuring and maintaining the linked vCenter Server instances requires careful planning and coordination. It may require additional networking and infrastructure considerations, such as network connectivity between the vCenter instances and proper firewall rules.
- Increased Dependency: When using Enhanced Link Mode, the availability and proper functioning of the linked vCenter Server instances become critical. If any of the linked vCenter Server instances experience issues or downtime, it can impact the management and operations of the entire vSphere environment. This increased dependency on the linked instances may introduce a higher risk of failure if proper redundancy and failover mechanisms are not in place.
- Licensing and Costs: Enhanced Link Mode requires the appropriate licensing and version compatibility across the linked vCenter Server instances. Depending on your specific licensing agreements and requirements, additional costs may be associated with enabling and utilizing Enhanced Link Mode. Considering the licensing implications and potential financial impact before implementing ELM is important.
- Potential Performance Impact: Linking multiple vCenter Server instances through Enhanced Link Mode can introduce additional network traffic and communication overhead. This can potentially impact the overall performance of vCenter operations and management tasks. Proper network design and capacity planning are essential for optimal performance when using ELM.
- Compatibility and Versioning Constraints: ELM requires that all linked vCenter Server instances run compatible versions and are part of the same vSphere version family. Upgrading or patching vCenter Server instances in a linked mode environment may require careful planning and coordination to ensure compatibility and avoid disruption to the infrastructure.
- Administrative Overhead: Managing multiple linked vCenter Server instances introduces additional administrative overhead. Configuring and maintaining settings, permissions, and configurations across multiple instances may require more time and effort than managing a single vCenter Server. It’s important to consider the availability of skilled administrators and the impact on operational processes.
It’s essential to evaluate these potential disadvantages against your virtual infrastructure’s specific needs and requirements before deciding to implement Enhanced Link Mode in vCenter Server. Proper planning, understanding, and consideration of these factors can help mitigate potential downsides.