Scenario: Suppose a company called XYZ Corporation heavily relies on virtualization technology for its IT infrastructure. They have many virtual machines running critical applications, and a vCenter Server manages these virtual machines.
XYZ Corporation has decided to implement vCenter HA to ensure high availability and minimize downtime. Here’s how the scenario unfolds:
- Initial Setup:
- XYZ Corporation has a primary vCenter Server deployed, which serves as the central management point for all virtual machines.
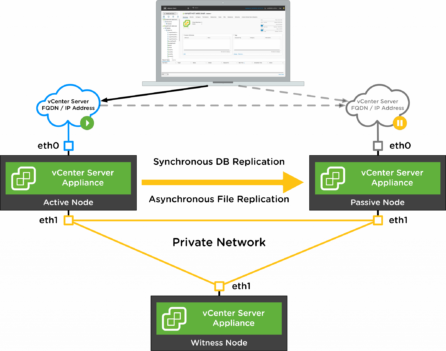
- They set up a vCenter HA cluster consisting of three ESXi hosts. This cluster is separate from their regular virtual machine cluster.
- They designate one of the ESXi hosts as the primary node, another as the secondary node, and the third as a witness node.
- Configuration and Deployment:
- The vCenter HA configuration wizard sets up the vCenter HA cluster. This involves specifying the primary and secondary node details, configuring network settings, and providing information about the witness node.
- Once the configuration is complete, the vCenter HA cluster is deployed, and the primary node becomes the active vCenter Server.
- Monitoring and Failover:
- The vCenter HA cluster continuously monitors the health and availability of the primary node. If the primary node becomes inaccessible or experiences a failure, the secondary node takes over and becomes the active vCenter Server automatically.
- During this failover process, the virtual machines and management services seamlessly transition to the secondary node, ensuring uninterrupted access to the virtual infrastructure.
- The witness node plays a critical role in the failover process by maintaining the state of the primary and secondary nodes. It helps determine if a failover is required and prevents split-brain scenarios.
- Failback and Recovery:
- After the failover occurs, the secondary node becomes the active vCenter Server, and the failed primary node can be repaired or replaced.
- Once the primary node is restored, it rejoins the vCenter HA cluster and becomes the secondary node. The cluster resumes its active-passive configuration.
- During this process, any changes made to the virtual infrastructure while the secondary node was active are synchronized back to the primary node, ensuring consistency.
- Ongoing Operations:
- XYZ Corporation continues using the vCenter HA cluster to manage its virtual infrastructure.
- Regular maintenance, updates, and backups are performed on the primary and secondary nodes to ensure the reliability and recoverability of the vCenter environment.
- In case of a planned downtime event, such as maintenance or upgrades, the vCenter HA cluster can be temporarily disabled, and the virtual machines can be manually managed through the secondary node.
By implementing vCenter HA, XYZ Corporation ensures that their vCenter Server remains highly available, reducing the risk of disruptions to their virtual infrastructure and enabling efficient management of their critical applications.
Benefits of vCenter HA
The primary benefit of vCenter HA configuration is increased availability and improved resilience for the vCenter Server. By deploying vCenter HA, you can minimize the impact of vCenter Server downtime and ensure uninterrupted management and control of your virtualized environment. Here are some specific advantages:
- Continuous availability: vCenter HA enables continuous availability by automatically providing failover capabilities for the vCenter Server. If a hardware or software failure of the active vCenter Server, vCenter HA will automatically and seamlessly switch over to a standby vCenter Server. This ensures that critical management functions remain operational without interruption.
- Enhanced Resilience: With vCenter HA, you can improve the resilience of your vCenter Server infrastructure. The standby vCenter Server continuously replicates the data, configuration, and state information from the active vCenter Server. This replication ensures a seamless takeover with minimal data loss or downtime. The standby server is fully equipped to step in during a failover situation.
- Simplified Management: vCenter HA simplifies the management of the vCenter Server infrastructure. The configuration and failover process is automated, eliminating the need for manual intervention during failover events. This saves time and reduces the potential for human errors in handling failover scenarios.
- Scalability and Performance: vCenter HA supports the deployment of vCenter Server in a cluster, allowing you to take advantage of the load-balancing capabilities. This enhances the scalability and performance of the vCenter Server, especially in larger environments with multiple hosts and virtual machines.
- Protection against Hardware and Software Failures: By implementing vCenter HA, you can protect your vCenter Server against hardware failures, such as server crashes or network outages, as well as software failures, like database corruption or application crashes. vCenter HA detects these failures and automatically initiates failover, ensuring minimal impact on management operations.
- Non-Disruptive Upgrades: vCenter HA simplifies upgrading your vCenter Server infrastructure. During an upgrade, the active vCenter Server can be taken offline, and the standby server takes over seamlessly, ensuring uninterrupted management and control of your virtualized environment.
Overall, vCenter HA provides a robust and reliable solution for ensuring high availability and resilience for the vCenter Server. By implementing vCenter HA, you can minimize downtime, improve operational efficiency, and enhance the overall stability of your VMware virtualization infrastructure.
Other configurations with similar advantages
- vCenter Server with Backup and Restore: Implementing a comprehensive backup and restore strategy for your vCenter Server can provide resilience. Regularly backing up the vCenter Server database, configuration, and certificates allows you to recover from failures or disasters. By combining this approach with efficient backup scheduling and periodic testing of the restore process, you can minimize downtime and maintain operational continuity.
HA requirements
- vSphere Cluster: You must have a vSphere cluster with at least three ESXi hosts. The vCenter HA nodes require this cluster to ensure high availability and failover capabilities.
- Shared Storage: A shared storage solution is required for vCenter HA. The shared storage replicates data, configuration, and state information between the active and passive vCenter HA nodes. Ensure that the shared storage is accessible to active and passive nodes.
- Network Configuration: The network configuration is crucial for vCenter HA. The active and passive vCenter HA nodes should be on the same network subnet to allow for communication and replication. Additionally, ensure the network supports the required bandwidth and latency for efficient data replication.
- IP Addressing: Each vCenter HA node must have a static IP address. You need to allocate three IP addresses: one for the active node, one for the passive node, and one for the vCenter HA witness appliance.
- NTP Configuration: Proper time synchronization is essential for vCenter HA. Ensure all vCenter HA nodes are synchronized with a reliable Network Time Protocol (NTP) server to avoid time-related issues.
- DNS Configuration: Configure DNS properly to ensure name resolution for the vCenter HA nodes. Each node should have a unique hostname and be resolvable via DNS.
- Firewall Rules: Check and configure the necessary firewall rules to allow communication between your environment’s vCenter HA nodes and other components. Ensure that the required ports are open for proper operation.
- Administrative Access: You need administrative access to deploy and configure vCenter HA. This includes sufficient privileges to create and manage virtual machines, clusters, and network settings.
Configuring HA
- Preparing the Environment:
- a. Ensure you have a vSphere cluster with at least three ESXi hosts. The vCenter HA feature requires a cluster to provide high availability and failover capabilities.
- b. Set up shared storage that is accessible to all hosts in the cluster. This shared storage will be used for data replication between the active and passive vCenter HA nodes.
- c. Verify that the network connectivity and firewall rules are correctly configured to allow communication between the vCenter HA nodes.
- Deploying the vCenter HA Nodes:
- a. Deploy the first vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) as the active node. This involves deploying the VCSA OVA file, specifying the necessary configuration details, and configuring the network settings.
- b. Deploy the second VCSA as the passive node. Like the active node, deploy the VCSA OVA file and configure the necessary settings. Make sure to specify the active node’s IP address during the deployment process.
- c. Deploy the vCenter HA witness appliance, which acts as a tiebreaker in split-brain scenarios. This appliance is automatically deployed and configured during the vCenter HA setup process.
- Configuring vCenter HA:
- a. Access the active node’s vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface (VAMI) using the configured IP address. Log in with appropriate administrative credentials.
- b. Navigate to the “High Availability” tab and click “Configure.” This will start the vCenter HA configuration wizard.
- c. In the configuration wizard, select the vSphere cluster where you want to enable vCenter HA and choose the shared storage data store.
- d. Provide IP addresses for the active and passive nodes. You can either use static IP addresses or configure DHCP reservations.
- e. Validate the network settings and review the configuration summary. Click “Finish” to begin the vCenter HA configuration process.
- f. The active node will be reconfigured, and the passive node will be set up as a clone of the active node. Data replication between the nodes will begin.
- Verifying the Configuration:
- a. Monitor the vCenter HA configuration process through the vSphere Web Client or the VAMI of the active node. The progress can take some time, depending on the size of your environment and the amount of data being replicated.
- b. Once the configuration is complete, verify the status of the vCenter HA nodes. The active node should show “Active” status, and the passive node should show “Passive” status.
- c. Perform failover testing to ensure that the failover process works as expected. You can simulate a failure by powering off the active node and observing the automatic failover to the passive node.
Conclusion
VMware vCenter HA, or VCHA, may be more important now as more and more services are integrated to VMware through the vCenter. The vSphere VMs can always be managed as a last resort on the ESXi they are running, however, the integrated services can not.
Depending on your vCenter implementation strategy, it may be the right solution. If you manage several vSphere Clusters and storage arrays with one single vCenter, and outage on one vSphere cluster may keep you from managing the VMs and VMware services running on the other clusters. If this is the case, VCHA is, from my point recommended.