Introduction:
VMware Admission Control is crucial as it directly influences a cluster’s virtual machine provisioning and resource allocation. The decision to enable or disable Admission Control necessitates a thoughtful approach, considering your enterprise’s specific requirements, workloads, and resilience targets. This article aims to shed light on VMware Admission Control, its functionalities, and considerations that enterprise architects must consider before making their choice.
- What is VMware Admission Control?
VMware Admission Control is a feature that guarantees that sufficient resources are available to support virtual machines during both normal operations and failure scenarios. It is designed to maintain High Availability (HA) and Fault Tolerance (FT) for virtualized workloads. Admission Control prevents resource over-commitment, which could lead to performance degradation or system failures when unexpected resource demands arise.
- Types of Admission Control in VMware:
VMware offers three types of Admission Control mechanisms:
- Host-Based Admission Control: Evaluate available resources on each host within a cluster to determine if new virtual machines can be accommodated.
- Cluster Resource Percentage: Reserves a specific percentage of cluster resources for failover situations.
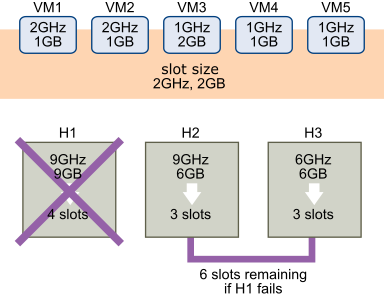
- Slot Policy: Based on the slot size, this method calculates the number of virtual machines that can be powered on in case of host failures.
- Factors to Consider Before Enabling VMware Admission Control:
- Workload Characteristics: Different workloads have varied resource demands. Understand the nature of your workloads to determine the right Admission Control mechanism.
- Cluster Size: The size of the cluster can impact the effectiveness of Admission Control. Smaller clusters may find it harder to allocate resources with particular mechanisms.
- Resilience Requirements: Consider the desired level of resilience. Some mechanisms, while ensuring resources during failure scenarios, might limit resource utilization.
- Resource Allocation Settings: Review the resource allocation settings for virtual machines and ensure they reflect accurate resource needs.
- Monitoring and Forecasting: Effective monitoring and capacity planning can help anticipate resource requirements and make informed Admission Control decisions.
- Pros and Cons of Enabling Admission Control:
- Benefits of Enabling Admission Control:
- Improved High Availability: With Admission Control, resource contention is minimized, leading to better HA support.
- Predictable Resource Allocation: Resource reservations enhance workload predictability and reduce the risk of performance degradation.
- Drawbacks of Enabling Admission Control:
- Overly Conservative Resource Allocation: In some cases, Admission Control may limit resource utilization more than necessary, leading to potential inefficiencies. ii. Complexity: Enabling and configuring Admission Control requires understanding its intricacies and impact on resource management.
Conclusion:
VMware Admission Control is a critical feature that ensures High Availability and Fault Tolerance of virtualized workloads. Architects should carefully evaluate their cluster’s characteristics, workload needs, and resilience requirements before deciding on enabling or disabling Admission Control, or which setting Admission Control should run with. If you decide not to run Admission Control, you in the role of the Admin or the Architect need to manually ensure you are not overcommitting the vSphere clusters.