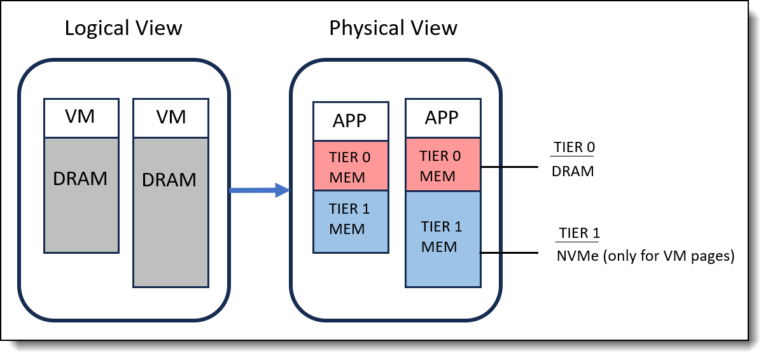
In VMware vSAN 8, we are introduced to the option of two different storage architectures.
OSA – Original Storage Architecture
ESA – Express Storage Architecture
What is ESA
vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA) uses a file system called Log-Structured File System (LFS). Log-structured File Systems belong to a class of file systems called no-overwrite file systems. The LFS design and on-disk layout attempts to convert all write operations into sequential I/O. The concept of LFS is to improve disc writing performance.
The log-structured file system writes data and metadata in an append-only fashion, essentially treating the disk as a circular log. It uses the write buffer technique and keeps track of all file updates in memory. When the buffer is sufficient, all changes are sequentially written to the disc in a free space.
The file system uses an inode data structure. Each inode contains the metadata of the reference file, such as owner, type, etc., as well as the address of the file on the disc. In addition, each inode has a unique identifier number. The inode map references this exclusive number to allocate the associated metadata. Because LFS writes sequentially, it keeps the inode together with its data blocks/segments.
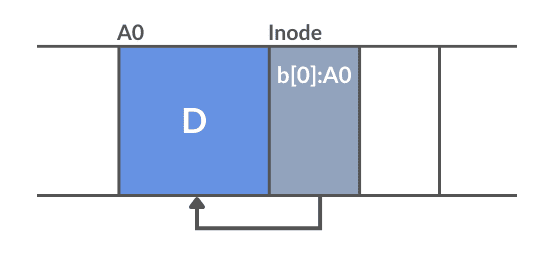
The File system uses the inode map to locate the inodes, and the map is updated every time it writes an inode to the disc with new location information. A buffer stores the active parts of the map, the other parts are divided into blocks and stored on the disc.
The segments are important parts of the LFS, these are units for reading, writing, and maintaining data. The system divides each segment into blocks of a fixed size. When the file system needs to write a new data it appends it to the end of the og in a new segment.
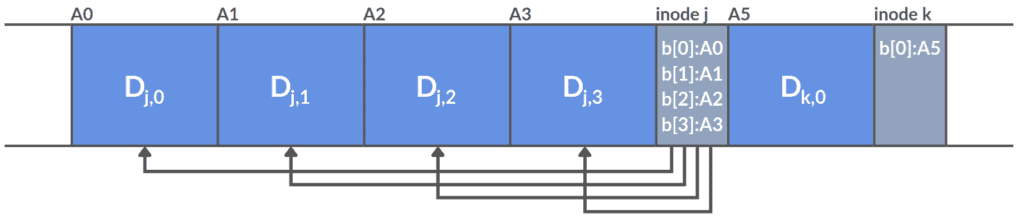
As LFS performs sequential writes these space on the disk must be available for the write operations to occur. LFS doesn’t remove file positions on the disk to write a new version. It always writes the lates version of a file to new locations. Old and no longer used version of files will take up space on the disk. To ensure freeing up disk the segment cleaning mechanism checks which segments are active and removes those that can be.
This mechanism periodically reads the old segments and identifies which blocks are active. It then compresses and reallocates only the active blocks into new segments elsewhere on the disk. This way, it reduces the space used on the disk and frees up the region of that segment for new writes.
Requirements for vSAN ESA
VMware vSAN ESA uses NVMe drives, higher CPU core counts, and high-speed networks to offer a simpler, more balanced design with higher overall performance.
To run vSAN ESA it is highly recommended to run nodes with at least 32 CPU Cores and at least 512GB of RAM. Disks have to be NVMe-based, Spinning drives and standard SSD are not supported. A 25GB network is the minimum requirement, however faster networks are encouraged.
The concept of disk groups as the data store building block is removed with VMware vSAN ESA. This removes the disk group as a failure domain, as the loss of the cache drive impacts the entire disk group. All storage devices operate independently when contributing to the pool. The architecture provides more flexibility, more resilience to hardware failure, more efficiency with a new log-structured file system, and better performance.
Check out the VMware vSAN ESA landing page for technical deep dives into the storage technology.