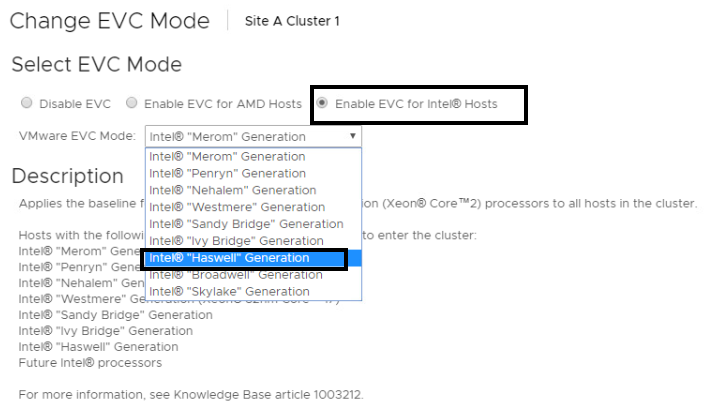
VMware EVC (Enhanced vMotion Compatibility) is a feature of VMware vSphere that ensures compatibility between hosts in a cluster when the hosts have different CPU generations or vendor architectures.
EVC presents a consistent set of CPU features to all virtual machines in the cluster, regardless of the underlying hardware. This allows virtual machines to be migrated between hosts with different CPUs without disrupting their operation.
When EVC is enabled, vSphere creates a baseline for CPU features that all hosts in the cluster must support. The cluster’s baseline is typically based on the oldest or most limited CPU, ensuring that all virtual machines can run on any host in the cluster.
EVC allows you to use mixed hardware in your cluster without worrying about compatibility issues. You can add new hosts with different CPUs to the cluster without upgrading all hosts to the latest CPU architecture. This can help you save costs and extend the life of your existing hardware.
EVC is particularly useful in scenarios where you need to perform maintenance or upgrades on individual hosts in the cluster, as it allows virtual machines to be migrated between hosts without downtime. EVC also simplifies cluster management by ensuring that virtual machines can be migrated to any host in the cluster, regardless of the underlying hardware.
Overall, VMware EVC is a valuable feature for ensuring compatibility between hosts in a vSphere cluster and simplifying the management of your virtualized environment.
Benefits
- Allows mixed CPU versions and models: With EVC mode enabled, you can use a mix of different CPU models and generations in the same cluster, which can help you save costs by allowing you to reuse older hardware. This can be especially useful if you run multiple workloads with varying resource requirements.
- Enables live migrations: With EVC mode, you can perform vSphere vMotion live migrations between hosts with different CPU generations and models within needing off the virtual machines.
- Simplifies management: EVC mode simplifies the management of your vSphere cluster, as you don’t need to worry about the compatibility of CPU generations and models. EVC mode masks the CPU capabilities of each host to ensure that the virtual machines running on them are compatible.
- Increases availability: By allowing live migrations between hosts with different CPU models and generations, EVC mode increases the availability of your virtual machines and reduces downtime. You can perform maintenance or upgrade activities on one host at a time while keeping your virtual machines running.
- Facilitates workload consolidation: EVC mode enables you to consolidate workloads onto a smaller number of hosts with different CPU models and generations, allowing you to use your hardware better and reduce power and cooling costs.
Disadvantages
- CPU performance: EVC mode may limit the performance of your virtual machines if you have hosts with newer CPUs in your cluster. Enabling EVC mode may mask the newer CPU capabilities, resulting in reduced performance for virtual machines that could otherwise benefit from newer CPU features.
- Licensing: Some CPU features may be required for specific software or applications you run in your virtual environment. In some cases, enabling EVC mode may mask these CPU features and result in noncompliance with licensing agreements.
- Maintenance: Enabling EVC mode may limit your ability to perform maintenance or upgrade activities on individual hosts in your cluster. For example, if you need to replace a host with a newer CPU, you may need to disable EVC mode to ensure the virtual machines can use the newer CPU features.
- Complexity: EVC mode adds complexity to your vSphere environment and requires careful planning and configuration. It may not be necessary if you have a homogeneous set of hosts with identical CPUs.
- Compatibility: EVC mode may not be compatible with third-party applications or services requiring specific CPU features. You should check with the vendor to ensure compatibility before enabling EVC mode.
While VMware EVC mode can be useful, it is not always necessary or appropriate for every vSphere environment. You should carefully evaluate your specific needs and requirements before deciding whether to enable EVC mode.
Conclusion
Within the VMware environments, I am responsible for. I do not mix different Server Configurations within a Cluster. I have, therefore, never really considered enabling this feature. However, there are most definitive use cases where it is highly recommended, especially if you have a different generation of CPU architecture.



thank you so much sir this is very good artcile